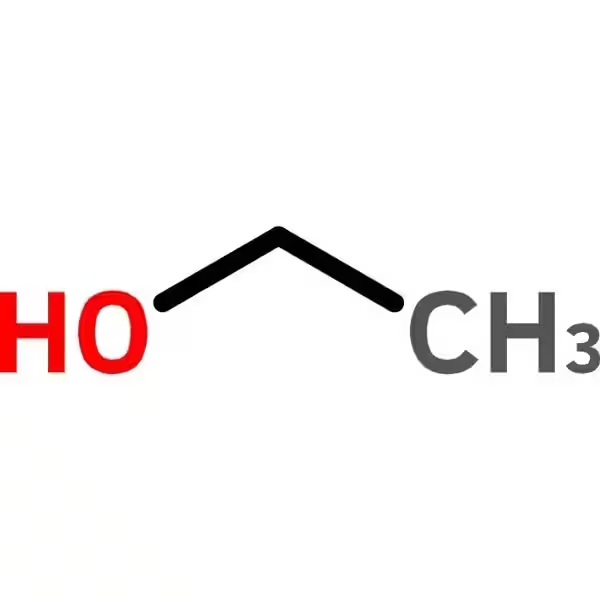
Methyl Alcohol CAS No: Understanding Methanol and its Applications

Understanding the chemical compound methanol, and its various applications and safety considerations, is crucial for anyone working with or around this substance. This article explores methanol, focusing on its CAS registry number (67-56-1) and what that signifies in terms of its availability, uses, and safety protocols.
What is Methyl Alcohol CAS No 67-56-1?
The CAS registry number 67-56-1 unequivocally identifies methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol. This unique identifier is essential for tracking the chemical throughout its lifecycle, from production to its final application. It allows researchers, industrial users, and regulatory bodies to pinpoint the exact chemical being discussed, eliminating ambiguity and ensuring correct identification.
This number is not just a label; it's a vital piece of information used in various databases and systems worldwide to access safety data sheets, regulatory information, and other critical details related to the handling and usage of methanol.
The significance of the CAS number lies in its universality. Regardless of the supplier, the nomenclature used, or the specific application, the CAS number 67-56-1 always refers to the same chemical compound: methanol. This consistent identification facilitates clear communication and prevents misunderstandings.
Methanol: Sources, Production, and Grades
Methanol, the simplest alcohol, has a rich history. Originally produced by the destructive distillation of wood – hence the name "wood alcohol"—modern industrial production involves the catalytic hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. This process yields vast quantities of methanol, making it a readily available and relatively inexpensive chemical.
However, the purity of methanol varies significantly. Large chemical suppliers like Sigma-Aldrich offer various grades, each tailored to specific applications. These grades are often categorized by purity levels, such as:
- Reagent Grade: Suitable for general laboratory use and educational settings.
- HPLC Grade: Characterized by exceptionally high purity and is used extensively in analytical chemistry, particularly in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
- Spectroscopic Grade: Meets stringent standards for use in spectroscopy, ensuring minimal interference with the analysis.
The packaging and available quantities also vary, ranging from small laboratory bottles to large industrial drums, catering to the needs of diverse users. The specific grade and packaging are critical considerations when purchasing methanol, as they directly impact cost and suitability for the intended application.
Applications of Methanol (Methyl Alcohol CAS No 67-56-1)
Methanol's versatility is reflected in its extensive range of applications across numerous industries:
Industrial Applications
-
Solvent: Methanol is a powerful solvent used in various chemical processes, from dissolving resins and polymers to extracting essential oils. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it indispensable in various industrial processes.
-
Fuel: Methanol has been explored as an alternative fuel source, both as a direct fuel and as an additive to gasoline. While its use as a direct fuel is limited, its incorporation as an additive can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
-
Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a crucial building block in the production of countless chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, and methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), a gasoline additive. Its role in these syntheses underlines its importance in the chemical industry.
Laboratory and Analytical Applications
-
Solvent in Analytical Chemistry: High-purity methanol, particularly HPLC grade, plays a critical role as a solvent and mobile phase in chromatography, enabling high resolution and precise separation of components in complex mixtures. Its use in analytical chemistry ensures accurate and reliable results.
-
Spectroscopy: Methanol of spectroscopic grade is essential in various spectroscopic techniques, minimizing interference and ensuring the accuracy of spectral analysis.
Safety and Handling of Methanol
Despite its wide range of applications, methanol is highly toxic. Ingestion of even small amounts can lead to serious health consequences, including blindness and death. Inhaling methanol vapors can also cause significant harm.
Therefore, safety is paramount when working with methanol. Strict adherence to safety protocols is mandatory:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, eye protection, and respirators, when handling methanol to minimize exposure risks.
-
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in work areas to prevent the accumulation of potentially harmful methanol vapors.
-
Storage: Store methanol in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Proper storage practices are vital for preventing accidents and preserving the integrity of the chemical.
-
Disposal: Dispose of methanol according to local and national regulations. Improper disposal can pose significant environmental and health hazards.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
The handling, storage, transportation, and disposal of methanol are subject to stringent regulations and safety standards. It is crucial to comply with all applicable local, national, and international regulations to ensure safe handling and minimize risks to both individuals and the environment. These regulations frequently vary depending on the quantity being handled and the end applications.
In conclusion, methyl alcohol (CAS No 67-56-1) is a versatile and widely used chemical, but its inherent toxicity demands careful handling and strict adherence to safety protocols. Understanding its properties, applications, and regulatory requirements is crucial for ensuring safe and responsible use. Always consult the relevant safety data sheets (SDS) and follow established guidelines when working with methanol.
Frequently Asked Questions about Methanol (CAS No. 67-56-1)
This FAQ provides general information about methanol (methyl alcohol). Specific details regarding purity, packaging, pricing, and availability will vary depending on the supplier and product grade. Always consult the supplier's Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for complete safety and handling information before working with methanol.
What is Methanol (CAS No. 67-56-1)?
Methanol (CH₃OH), also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest aliphatic alcohol. It's a colorless, volatile, flammable liquid with a characteristic odor. It's significantly more toxic than ethanol.
What are the common uses of Methanol?
Methanol has diverse applications, including:
- Solvent: In chemical processes, reactions, extractions, and purifications across various industries (pharmaceutical, chemical synthesis, materials science).
- Fuel: Used as a fuel or fuel additive, though its toxicity requires special handling and safety precautions.
- Chemical Intermediate: A precursor in the synthesis of numerous chemicals (formaldehyde, acetic acid, MTBE, etc.).
- Analytical Chemistry: High-purity methanol is crucial as a solvent and mobile phase in techniques like HPLC.
How toxic is Methanol?
Methanol is highly toxic. Ingestion can cause blindness or death. Its toxicity arises from its metabolism to formaldehyde and formic acid, which inhibit cellular respiration. Exposure should be avoided. Always consult the SDS for specific hazard information and safety precautions.
What are the safety precautions when handling Methanol?
Methanol is flammable and toxic. Appropriate safety measures are crucial:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves, eye protection, and respirators as recommended by the SDS.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent inhalation of fumes.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from ignition sources.
- Disposal: Dispose of according to relevant local, regional, and national regulations.
Where can I purchase Methanol?
Methanol is available from various chemical suppliers. Major suppliers often offer various grades of methanol with different purities and packaging options. It's vital to choose a grade appropriate for your intended application.
What are the different grades of Methanol available?
Suppliers typically offer different grades, such as reagent grade (general lab use), HPLC grade (analytical purposes), and other specialized grades with varying levels of purity. The specific grades and their specifications will vary depending on the supplier.
What is the difference between Methanol and Ethanol?
While both are alcohols, methanol (methyl alcohol) is significantly more toxic than ethanol (ethyl alcohol, the type found in alcoholic beverages). Ethanol is metabolized differently and is less harmful, while methanol's metabolites are highly toxic.
What are the regulatory aspects of Methanol?
Regulations regarding the handling, storage, transportation, and use of methanol vary by location. Always comply with all relevant local, regional, and national safety regulations and labeling requirements. The SDS will provide some guidance, but it's recommended to consult local authorities for detailed legal requirements.
Is Methanol used as a fuel?
Yes, methanol has been explored as a fuel source, both directly and as a fuel additive. However, its toxicity and flammability necessitate stringent safety measures. Its use as a fuel is more prevalent in certain industrial applications and niche vehicle types than in widespread consumer vehicles.
This FAQ provides a general overview. For detailed information on a specific methanol product, always refer to the supplier's documentation, including the Safety Data Sheet (SDS).